前言
上一篇我们了解了springboot启动的基本流程,但是留下了一些疑问,其中有个重要的方法refresh()今天我们重点针对性的分析一下,让我们先看一下refresh的定义,从注释可以看出这里一直在强调单例对象的创建,那我们上一篇文章留下的问题看来今天可以得到答案了
/**
* Load or refresh the persistent representation of the configuration, which
* might be from Java-based configuration, an XML file, a properties file, a
* relational database schema, or some other format.
*
* 从java配置类、xml文件、properties配置文件、数据库或者其他格式中加载或刷新配置的持久化
*
* <p>As this is a startup method, it should destroy already created singletons
* if it fails, to avoid dangling resources. In other words, after invocation
* of this method, either all or no singletons at all should be instantiated.
*
* 这个方法在启动的时候调用,所以如果失败了需要销毁已经创建的单例对象,
*
* @throws BeansException if the bean factory could not be initialized
* @throws IllegalStateException if already initialized and multiple refresh
* attempts are not supported
*/
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
结合UML类图看一下内部关系
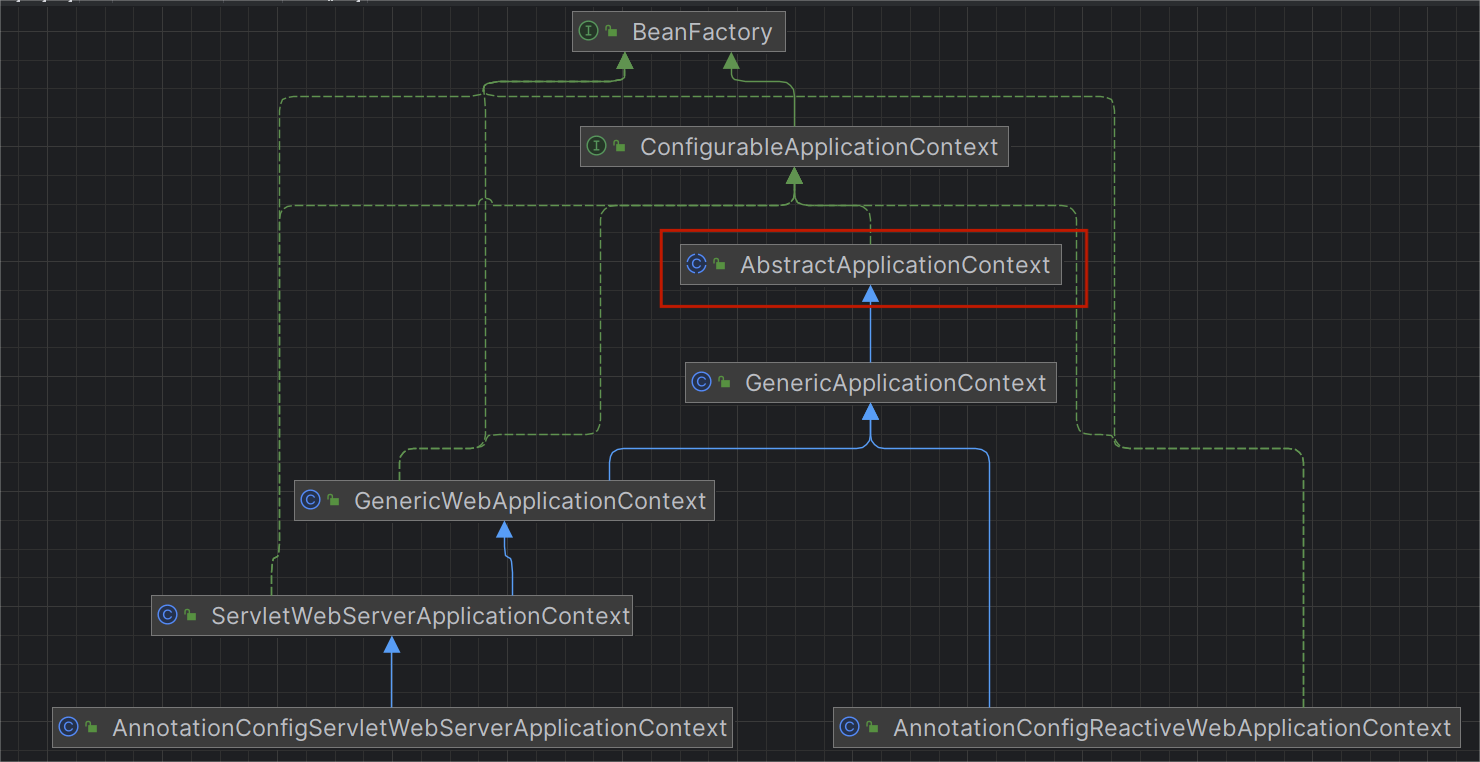
让我们把重心放到AbstractApplicationContext这个类的实现上来,除了ComplexWebApplicationContext和SimpleWebApplicationContext外,所有其他web容器都会调用这里的refresh方法来完成容器的初始化。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//在springboot中 比如是servlet容器,实际上先调用该类的子类AnnotationConfigServletWebApplicationContext.prepareRefresh方法
//这里面多做了一步ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.clearCache,先清空Map<Resource, MetadataReader> metadataReaderCache里的资源元数据,然后再调用这里的prepareRefresh
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//ConfigurableListableBeanFactory类实现对工厂的配置以及对bean属性的自动装配
//获取刷新后的工厂类
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//添加BeanPostProcessor-ServletContextAwareProcessor @see GenericWebApplicationContext#postProcessBeanFactory
//添加BeanPostProcessor-WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor @see ServletWebServerApplicationContext#postProcessBeanFactory
//注册scope到容器 @see RequestScope SessionScope
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口是Spring初始化BeanFactory时对外暴露的扩展点,BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以在容器实例化任何bean之前读取或修改bean的定义
//todo 方法较长 放到下一篇介绍
// 本着循序渐进 由浅到深的原则 先跳过这个方法 @see PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
// PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate是AbstractApplicationContext委托执行post processors任务的工具类
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor是有区别的 别搞混了,这个是对bean实例的扩展点,上面是bean定义的扩展点,作用于bean生命周期的不同时机
//注册BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
//初始化国际化资源,如果没有则注册一个DelegatingMessageSource到容器中,并作为属性messageSource的值
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//初始化ApplicationEventMulticaster,如果没有则注册一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster实例到容器中,并作为属性applicationEventMulticaster的值
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//默认是个空方法,所以是为了提高扩展性设计的,留了个口子供子类实现
//比如@see GenericWebApplicationContext#onRefresh 初始化了web项目的UI主题 前后端分离基本可以不用关心这个了
//比如@see ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh 在这里创建了一个web服务器
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
//获取所有ApplicationListener,注册所有的事件监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//准备动手,前戏已完成,现在开始实例化对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}流程
1.为上下文刷新做准备
/**
* AbstractApplicationContext#prepareRefresh
*
* Prepare this context for refreshing, setting its startup date and
* active flag as well as performing any initialization of property sources.
*/
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
//初始化标志位及启动时间
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
//看这些源码经常能看到这些日志打印的判断,减少在生产环境的资源消耗,同理会增加debug环境的资源消耗
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
//将enviroment.getPropertySources里的初始化资源{@see StandardEnvironment#customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources) } StubPropertySource替换为实际的资源
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:校验参数-不能为null
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
...
}2.获取单例对象工厂类
/**
* AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory
* Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
* @return the fresh BeanFactory instance
* @see #refreshBeanFactory()
* @see #getBeanFactory()
*/
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//抽象方法,子类去实现@see GenericApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()
refreshBeanFactory();
//获取工厂类实例 @see GenericApplicationContext#GenericApplicationContext()
//默认实现返回的是@see DefaultListableBeanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}/**
* GenericApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
*
* Do nothing: We hold a single internal BeanFactory and rely on callers
* to register beans through our public methods (or the BeanFactory's).
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
//先获取锁,只允许执行一次,然后初始化id
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}3.BeanFactory的初始化
这个方法粗略一看其实没什么内容,主要是做了一些属性的初始化,可以简单看一下里面的几个重要的属性,看起来都是在为bean的注入做准备
/**
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
//设置bean的类加载器
// 默认 ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader()
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
//设置默认表达式解析器
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//注册默认PropertyEditor,用于依赖注入时对参数的解析转换
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
//ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#ignoreDependencyInterface
//设置忽略自动装配的接口
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
//@see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#registerResolvableDependency
//注册可以自动解析注入的类,当一个接口有多个实现类时,可以通过这个方法明确注入哪个类
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
//设置BeanPostProcessor-ApplicationListenerDetector
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
//注册一些基本的bean
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}4.注册子类自定义的BeanPostProcess
5.实例化并调用所有已注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean
6.注册BeanPostProcessor到beanFactory
7.初始化国际化资源
8.初始化ApplicationEventMulticaster
9.调用onRefresh()
AbstractApplicationContext里只是一个空方法,留了个口子供子类进行扩展,比如这是ServletWebServerApplicationContext的实现
/**
*ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh
*
*/
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
//字面意思 创建web服务器
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
/**
* 创建服务器 并更新配置资源
*/
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//根据定义的工厂类生成web服务器,后面贴了一段工厂类配置示例
//todo tomcat容器怎么启动、运行、销毁的 后面再分析 先欠着
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
/**
*
*配置示例
*/
@Bean
public ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory webServerFactory() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
public void postProcessContext(Context context) {
SecurityConstraint securityConstraint = new SecurityConstraint();
securityConstraint.setUserConstraint("CONFIDENTIAL");
SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection();
collection.addPattern("/*");
collection.addMethod("HEAD");
collection.addMethod("OPTIONS");
collection.addMethod("TRACE");
collection.addMethod("COPY");
collection.addMethod("SEARCH");
collection.addMethod("PROPFIND");
securityConstraint.addCollection(collection);
context.addConstraint(securityConstraint);
}
};
tomcat.addConnectorCustomizers(new TomcatConnectorCustomizer[]{(connector) -> {
connector.setAllowTrace(true);
connector.setProperty("relaxedQueryChars", "|{}[]\\");
}});
return tomcat;
}10.注册时间监听器
11.开始初始化bean
/**
* Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory,
* initializing all remaining singleton beans.
*/
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
......
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
//即将进行初始化实例,加上标志 不允许修改bean定义
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//todo 这个也值得单独深入研究一下
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}12.完成contextRefresh
/**
* Finish the refresh of this context, invoking the LifecycleProcessor's
* onRefresh() method and publishing the
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent}.
*/
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
//清楚resource缓存
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
//从容器中获取lifecycleProcessor到上下文
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
//发布容器刷新完成事件
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}异常处理
到这里上下文刷新完成了,但是还要处理一下异常,如果创建bean失败了怎么办
销毁所有已经创建好的bean
修改标志位(prepareRefresh里设置的)



